Ph Pka Log A Ha
How to Derive Henderson Hasselbalch Equation?
Henderson-Hasselbalch equation is a simple expression which relates the pH , pKa and the buffer activeness of a weak acid and its cohabit base. The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation also describes the characteristic shape of the titration curve of whatever weak acid such as acerb acid, phosphoric acid, or any amino acrid. The titration curve of a weak acid helps to determine the buffering pH which is exhibited around the pKa of that acrid.
For case, in the instance of acetate buffer, the pKa is 4.76. This is the best buffering pH of acetic acid. Besides, at this pH the acerb acid (CHiiiCOOH) and acetate ions (CH3COO¯) volition be at equimolar concentration in the solution. This equimolar solution of a weak acid and its conjugate base of operations will resist the change in pH past altruistic or taking upward the H⁺ ions. ( pH is the negative logarithm of hydrogen ion concentration in a medium. The pKa is the negative logarithm of Ka. The Ka is the dissociation abiding (similar to the equilibrium constant) for the ionization reaction of an acrid.)
Learn more: Titration Bend of a Weak Acid (Acetic Acid)
In the nowadays post, we will see the derivation of Henderson-Hasselbalch equation from the ionization reaction of a weak acrid. We also discuss the significance of Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
Deriving Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation
Accept the ionization reaction of a weak acrid (HA):
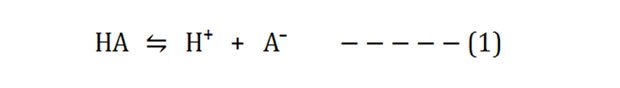
The dissociation constant Ka of the above reaction volition be:
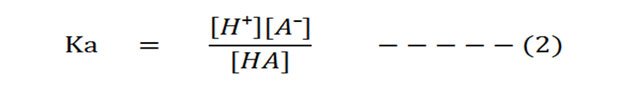
Dissociation constant is the ratio of the concentration of products by the concentration of reactants. The square brackets, [ ], denote 'concentration'.
So from the equation (ii) have out the [H⁺] to the left side (solve for H⁺):
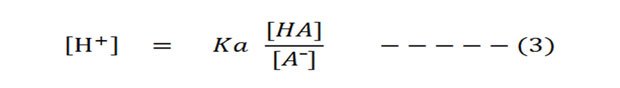 And so accept the negative logarithm of both sides:
And so accept the negative logarithm of both sides:
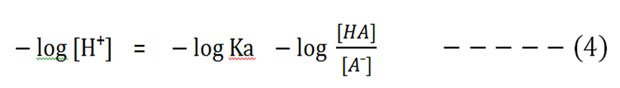
We know that the – log [H⁺] is pH and the – log Ka is pKa.
Substitute the pH and pKa in the equation (4):
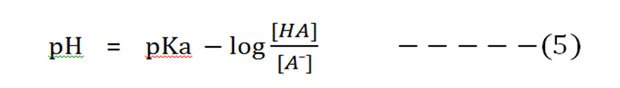
Now invert the -log [HA]/[A¯], which involves changing its sign to obtain the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
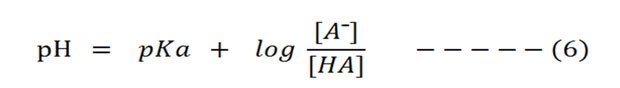
[A¯] is the concentration of proton acceptor (information technology can accept the proton in a buffer)
[HA] is the concentration of proton donor (it can donate a proton in the buffer)
Thus the equation (six) can exist amend stated every bit:
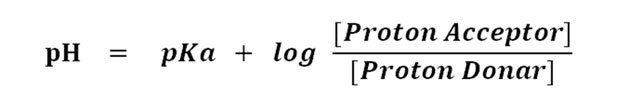
The above equation is called the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
Uses of Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation
The Henderson–Hasselbalch is mainly used for calculating the pH or pKa of a solution containing known quantities of a weak acrid and its conjugate base.
Learn more: Biochemistry Solved Problems – pH, pKA and Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation.
At the midpoint of the titration curve of a weak acrid, the concentration HA (proton donor) equals the concentration of A¯ (proton acceptor). We accept already stated that for a buffer the best buffering pH is at its pKa. (Likewise remember, the buffer is a mixture of equimolar concentration of weak acid and its cohabit base).
Let's put it in the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation
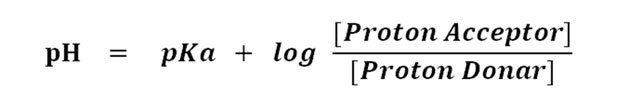
Since the concentration of proton acceptor (A¯) and proton donor (HA) is uniform in the midpoint of titration, the value becomes log 1.
Thus the equation becomespH = pKa + log 1
log 1 = 0
ThuspH = pKa + 0
= pH = pKa
This besides proved that for a buffer, the best buffering activity is obtained at the pH value equal to its pKa value.
References: Lehninger A.B., (2018), Textbook of Biochemistry, Ed. v, Pearson International, New York
Report Offline (Without Net)
Now you lot can Download the PDF of this Post Absolutely Gratis !
Please click on the Download Link / Button beneath to Save the postal service every bit a Single PDF file. The PDF file will be opened in a new window in the browser itself. Correct click on the PDF and select 'Save As' selection to save the file to your figurer.
Please Share the PDF with your Friends, Relatives, Students and Colleagues…

<< Back to Biochemistry Lecture Notes
You might also like…
@. Titration Curve of Weak Acid
@. Workout Issues of pH and pKa using Henderson Hasselbalch Equation
@. Concrete and Biological Properties of Water
@. Why the pH of water is 7?
@. How Hydrogen Bond is formed in Water?
@. Proton Hopping in H2o
More than Biochemistry Lecture Notes…

bygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({});
Ph Pka Log A Ha,
Source: https://www.easybiologyclass.com/ph-and-pka-henderson-hasselbalch-equation-deriving/
Posted by: connoragoeme.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Ph Pka Log A Ha"
Post a Comment